The chair of this working group is:
 Dr.Zoran Atansov, Doctor Veterinary Medicine. Current employer Institute of Accreditation of Republic N.Macedonia. Advisor-Coordinator for accreditation on laboratories for calibration of instruments. Prime minister personnel adviser for Agriculture, Food Safety, Veterinary and Phytosanitary Policy 2020-2021. Director of Food and Veterinary Agency , 2017-2020 year. Until 2022 he was at the Accreditation Institute, and from 2023 he works as an advisor at the Agency for Financial Support in Agriculture and Rural Development
Dr.Zoran Atansov, Doctor Veterinary Medicine. Current employer Institute of Accreditation of Republic N.Macedonia. Advisor-Coordinator for accreditation on laboratories for calibration of instruments. Prime minister personnel adviser for Agriculture, Food Safety, Veterinary and Phytosanitary Policy 2020-2021. Director of Food and Veterinary Agency , 2017-2020 year. Until 2022 he was at the Accreditation Institute, and from 2023 he works as an advisor at the Agency for Financial Support in Agriculture and Rural Development
Elected member of EU FMD Executive Committee in period 2018 -2020. Founder of “Supply Chain Management Consortium – Macedonia”, giving training and consultancy to companies as AD ALKALOID, AD TIKVES, USAID, UNMIK, NODUS, Faculty of Technology Science in Skopje in field of Supply Chain Management. Two decades of experience in risk assessment and management of Food and Feed Safety, Animal Health and Welfare. One decade of experience in logistics operations, planning and analyses. Chairman of Steering Committee on IPA project “Improved implementation of animal health, food safety and phytosanitary legislation and corresponding information systems”. One of the creators of Doctrine for “National Logistic Support to Ministry of Defense and Army “. Additional training and coaching: ” Lieders of 21 st century“ – George C Marshal Center, Garmisch Partenkirchen Germany; Recourse management Planning and implementation of finance and material recourses QUEEN’S SCHOOL OF BUSINESS – Ottawa, Canada; Food Safety / HACCP UNITED STATES DEPARTMENT OF AGRICULTURE Cochran Fellowship Program North Dakota University Fargo, U.S.A; Official control of animal origin food, microbiological criteria and sampling – Agriconsulting Europe S.A; Traces and Official control of animal origin food on Border control point – BFST , Talin -Estonia.
Expert in EU Regulative:
Regulation 178/2002 general principles and requirements of food law, establishing the European Food Safety Authority and laying down procedures in matters of food safety
Regulation 1774/2002 health rules concerning animal by-products not intended for human consumption
Regulation 1831/2003 additives for use in animal nutrition
Regulation 852/2004 hygiene of foodstuffs
Regulation 882/2004 on official controls performed to ensure the verification of compliance with feed and food law, animal health and animal welfare rules
Regulation 183/2005 requirements for feed hygiene
Regulation 396/2005 Plant Health & Pesticides Residues
Regulation 2073/2005 on microbiological criteria in foodstuffs
Regulation 1331/2008 common authorization procedure for food additives, food enzymes and food flavorings
Regulations 1333/2008 food additives
Regulation 767/2009 placing on the market and use of feed
Regulation 1169/2011 provision of food information to consumers
Regulation 2016/429 on transmissible animal diseases and amending and repealing certain acts in the area of animal health
Regulation 2017/625 – Official controls and other official activities performed to ensure the application of food and feed law, rules on animal health and welfare, plant health and plant protection products.
Regulation 2019/6 Veterinary medicine product
Regulation 1/2005 protection of animals during transport and related operations
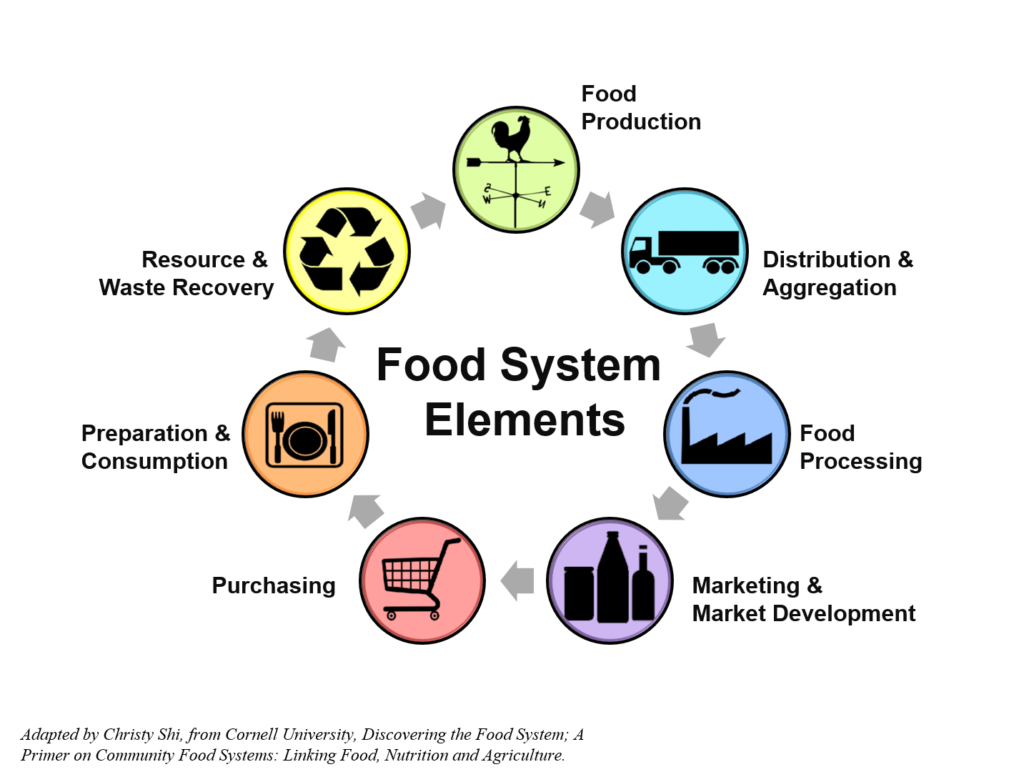
The “Food and Feed Safety, Logistics and Supply Chain” working group plays a vital role in ensuring the safety, quality, and efficient distribution of food and feed products. Here are key actions and initiatives in EU projects that the working group will consider:
- Regulatory Compliance: Stay updated on local and international food and feed safety regulations and standards. Ensure that all members of the supply chain are in compliance with these regulations.
- Risk Assessment: Conduct comprehensive risk assessments to identify potential hazards in the food and feed supply chain. This includes assessing risks related to contamination, spoilage, and transportation.
- Traceability: Implement traceability systems to track the movement of food and feed products throughout the supply chain. Utilize technologies like blockchain to enhance transparency and traceability.
- Quality Assurance: Establish quality assurance programs to maintain high product quality standards at every stage of the supply chain, from production to distribution.
- Food Safety Training: Provide training and education on food safety best practices to workers and stakeholders across the supply chain. Ensure that everyone involved understands their roles in maintaining safety.
- Hygiene and Sanitation: Promote and enforce strict hygiene and sanitation practices in food and feed processing facilities, storage, and transportation.
- Testing and Analysis: Implement routine testing and analysis of food and feed products for contaminants, pathogens, and other quality parameters. Ensure quick and accurate reporting of results.
- Recall Plans: Develop comprehensive recall plans and protocols to respond quickly to any food or feed safety issues. Test these plans periodically to ensure effectiveness.
- Supply Chain Efficiency: Identify areas for improvement in the supply chain to reduce waste, lower costs, and improve overall efficiency. Streamline logistics and distribution processes.
- Cold Chain Management: If applicable, implement and manage cold chain logistics to maintain the freshness and safety of perishable food products.
- Collaboration and Communication: Foster collaboration and communication among supply chain stakeholders, including producers, processors, distributors, retailers, and regulatory bodies.
- Food Defense: Implement measures to protect the food and feed supply chain from intentional contamination or tampering.
- Emerging Technologies: Stay abreast of emerging technologies such as IoT (Internet of Things), AI (Artificial Intelligence), and data analytics to enhance supply chain management, detect anomalies, and improve safety.
- International Standards: If involved in international trade, ensure that products meet the food and feed safety standards of the countries or regions where they are exported.
- Crisis Management: Develop crisis management plans for handling unexpected disruptions, such as natural disasters or global health crises, to maintain the continuity of the supply chain.
- Sustainability: Promote sustainability practices within the supply chain, including reducing food waste, minimizing packaging, and adopting eco-friendly transportation options.
- Consumer Education: Educate consumers about safe food handling practices and the importance of checking for product recalls or safety alerts.
- Research and Development: Invest in research and development to discover new technologies and methods for enhancing food and feed safety and supply chain efficiency.